-
An infinitesimal change in a variable or an infinitesimal change in a function resulting from a small change in the variable(s).
For example, if f(x) = 2x, then a change in f(x),
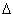 f, resulting from a small change in x,
f, resulting from a small change in x,  x, would be
x, would be  f = f(x+
f = f(x+ x) - f(x) = 2(x+
x) - f(x) = 2(x+ x) - 2x = 2
x) - 2x = 2 x. The differential df is defined as the limit of
x. The differential df is defined as the limit of  f as
f as  x approaches infinitely small. In the above example, the differential is also called total differential because it takes into account changes in all of the variables (just one in this case). The derivative df/dx can be thought of as a ratio of two differential changes.
x approaches infinitely small. In the above example, the differential is also called total differential because it takes into account changes in all of the variables (just one in this case). The derivative df/dx can be thought of as a ratio of two differential changes.For a function with more than one variable, such as f(x,y) = 2xy, the change in f(x,y) resulting from a change in x,
 x, while keeping y constant, is called the partial differential:
x, while keeping y constant, is called the partial differential: f(x+
f(x+ x,y) - f(x,y) = 2(x+
x,y) - f(x,y) = 2(x+ x)y - 2xy = 2
x)y - 2xy = 2 x y
x yThe rate of change of f(x,y) with respect to x only is called the partial derivative.